Invertible Matrix Columns Linearly Independent
Not changed if adding a multiple of one row columns to another row columns. To deal with the case you specifically offer lets use a 3x2 matrix.

Understanding A Proof For A Square Matrix Is Invertible If Its Rows Are Linearly Independent Mathematics Stack Exchange
So vectors A u 1 v 1 A u 2 v 2 and A u 3 v 3 are linearly independent and v 1 a 11 a 21 a 31 v 2 a 12 a 22 a 32 and v 3 a 13 a 23 a 33.

Invertible matrix columns linearly independent. IfX isaleftinverseofAthen Ax b x XAx Xb thereisatmostonesolutionifthereisasolutionitmustbeequaltoXb Right-invertible matrix. R n R n be the matrix transformation T x Ax. Therefore by the Invertible Matrix Theorem Pb is invertible.
C Write the vector mathbfb as a linear combination of mathbfA_1 mathbfA_2 and mathbfA_3. So column linear independence is most essentially about injectivity of the transformation. A simple way to see this is to recall that the matrix-vector product produces a vector that is the sum of the columns of weighted by the entries of.
The following statements are equivalent. Polynomial unimodular matrix. CL d of the matrix D.
Find a standard matrix for the orthogonal projection of Rn onto the row space of A. Properly independent set is AK-linearly independent. All four conditions from a to d are therefore equivalent.
Explain why the columns of an nxn matrix A are linearly independent when A is invertible. In particular when has linearly independent columns and thus matrix is invertible can be computed as A A A 1 A. In more detail if has columns and has entries then is the vector.
The columns of A span R n. The inverse of a matrix Cofactor C ij is 1ij times the determinant of the minor matrix M obtained from of the matrix A. Ax b has a unique solution for each b in R n.
The rank r is determined. We want to solve the vector equation. Now let f be a pxm injective transfer matrix ie with linearly independent columns and let f N-1.
The proof proceeds by circularly proving the following chain of implications. AU- AY is any polynomial matrix then there exists a polynomial unimodular matrix M. If kn so more columns than rows it is impossible to make the matrix linearly independent.
Well by the definition of a basis the column vectors of Pb are linearly independent. The columns of an invertible nxn matrix are linearly independent and span Rn so they form a basis for Rn 23 Row operations do not affect linear dependence relations among the columns of a matrix. There will not be enough pivot columns to fill each column.
Let A be an m n matrix with linearly independent row vectors. Displaystyle AleftAAright-1A This particular pseudoinverse constitutes a left inverse since in this case A A I displaystyle AAI. Since AA-1 1 A must have linearly independent columns.
We know that the column vectors of an invertible matrix are linearly independent. Thus the vectors mathbfA_1 mathbfA_2 mathbfA_3 are linearly independent. The concept of proper bases has found many applications in mathematics as well as in system theory see 8 11 12 26 and 27.
H Rectangular matrix the columns of which are successive second difference vector h H Transpose of H H Generalized inverse h h Second difference vector h0 Initial second difference vector of a sequence I Identity matrix J Jordan Canonical form for A. Choose the correct answer below. Evaluation of matrices by consecutive reduction to smaller sizes.
Is invertibleThenAis square and its columns are linearly independentLet be the number of columnsThen rankAn. A has n pivots. Linearly independent to specified tolerance.
Is it OK if I now define another transformation lets say B. Solving the matrix equatiion Ax 0 will either verify that the columns v 1 v 2 v k are linearly independent or will produce a linear dependence relation by. Let A be an m n matrix with linearly independent columns and let A QR be a QR factorization of A.
Let A be an n n matrix and let T. Be a zero representation of f. A A can be reduced to the identity by a sequence of elementary row operations.
Basis vectors for V are columns of matrix A and are linearly independent. A b c d a. Show that A and Q have the same column space.
The columns of a square matrix A are linearly independent if and only if A is invertible. IfA isinvertiblethen Ax b x A1b. Such that the columns.
The columns of A are linearly independent. If two columns or rows are identical then jAj 0. IfX isarightinverseofAthen x Xb Ax AXb b thereisatleastonesolutionnamelyx Xb Invertible matrix.
A has nullity 1 The columns are linearly independent The matrix is not invertible O The matrix has determinant - 1 -2 3 2 Find the rank of the matrix A 2 3 6 6 -2 -5 1 O 2 3 O Let which of the following is abasis of the null space of A 100010 001. IfA is invertible then A has an inverse matrix A-7. There exists an.
Linear equations and matrix inverse Left-invertible matrix.

Showing That A Transpose X A Is Invertible Matrix Transformations Linear Algebra Khan Academy Youtube

8 Linear Algebra 1 1 2 21 Let A 1 2 3 3 1 And Chegg Com

Invertible Matrix Theorem Youtube

Mathematical Fundamentals Linear Algebra Jothi Ramalingam Jothiramnitk Edu

Lesson Plan Template High School Inspirational Lesson Plan Template High School Math Lesson Plans Template Lesson Plans Template High School Math Lesson Plans
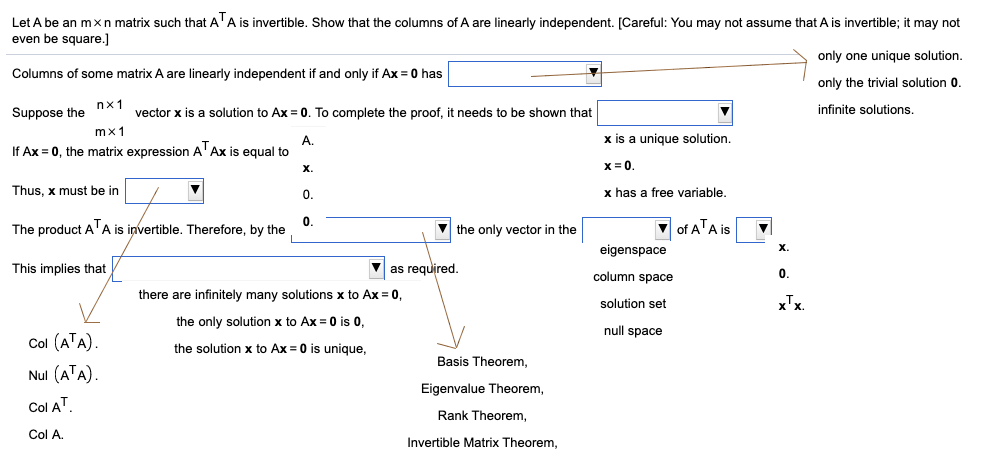
Let A Be An Mxn Matrix Such That Ata Is Invertible Chegg Com
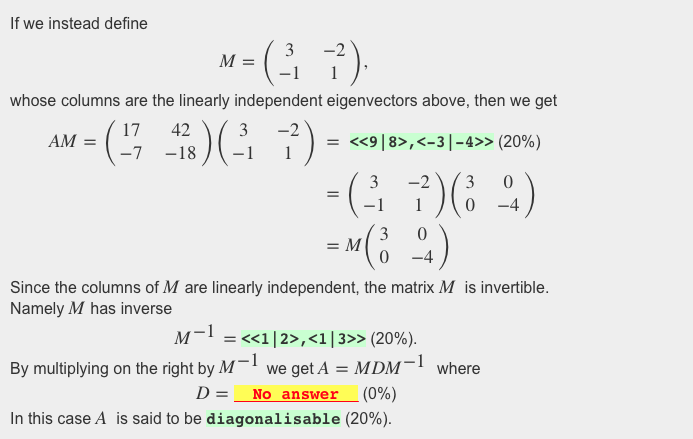
Solved If We Instead Define Whose Columns Are The Linearl Chegg Com

Answered If A A Is An Invertible Matrix Then Bartleby

Matrix Inverse And Linear Dependence Mathematics Stack Exchange
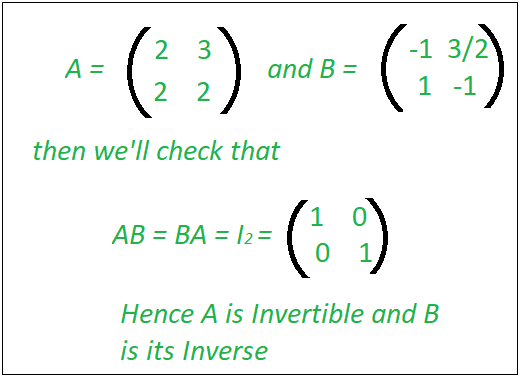
Check If A Matrix Is Invertible Geeksforgeeks

Check The Statements Below That Are True The Chegg Com
If A Is Invertible Then The Columns Of A Are Chegg Com

Null Space 3 Relation To Linear Independence Video Khan Academy

If The Rank Of A 5x6 Matrix Q Is 4 Then Which One Of The Following Statements Is Correct Gate Youtube

Matrix Inverse And Linear Dependence Mathematics Stack Exchange
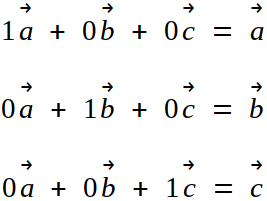
Part 8 Linear Independence Rank Of Matrix And Span By Avnish Linear Algebra Medium

Left Right Linear Independence In Quaternion Matrix Mathematics Stack Exchange

The Inverse Of A Matrix Linear Algebra Geometry And Computation
